Can You Install a Level 3 EV Charger at Home? 2025 Expert Guide & Best Solutions
Introduction
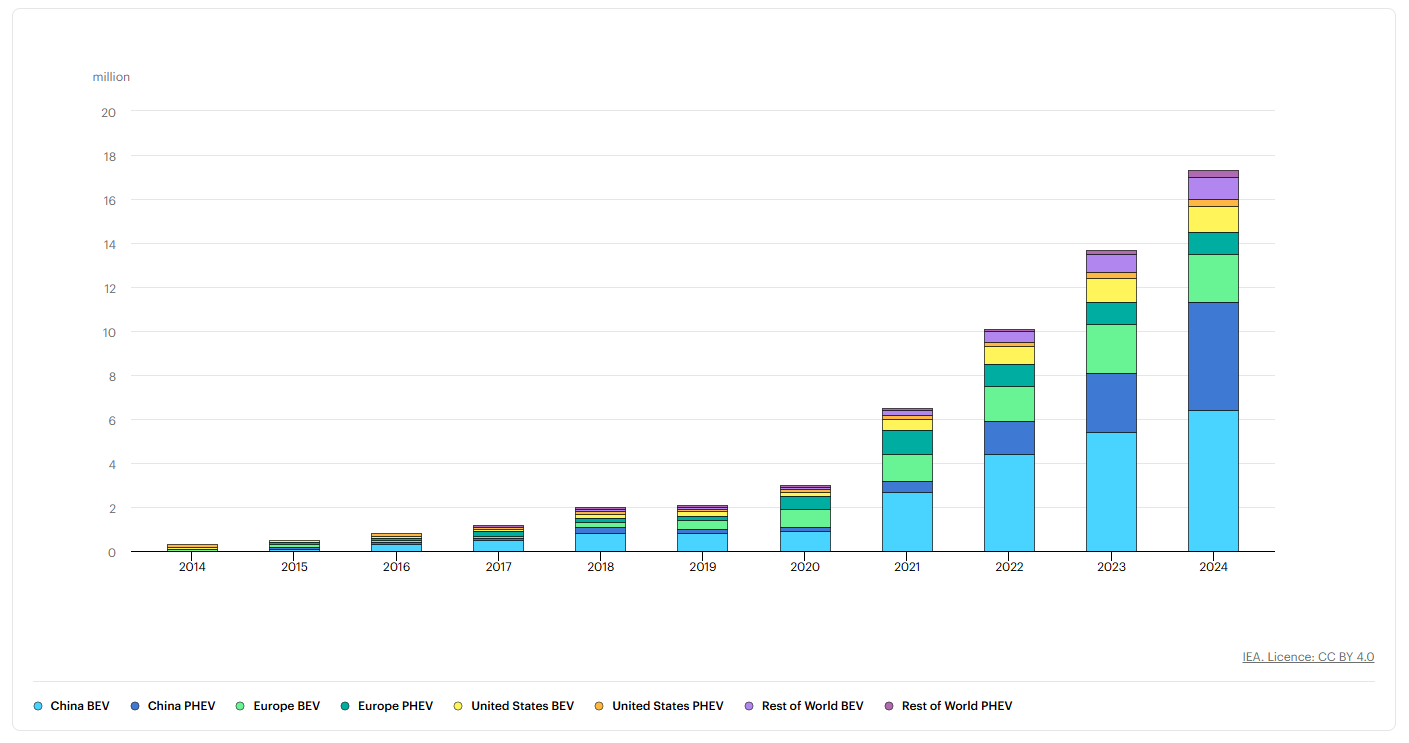
Global electric vehicle ownership just passed 32 million (IEA, 2025). And more EV owners are asking the same question: “Can I install a Level 3 EV charger at home?” Let’s be real—public fast charging stations have long lines. Holiday “charging crunches” are a nightmare. The thought of a “30-minute full charge in your garage” sounds amazing. But here’s the truth: it’s not that simple.
This guide breaks down the feasibility of a Level 3 EV charger at home using 2025’s latest electrical codes, home infrastructure data, and cost numbers. We’ll also show you the best home EV charging solutions—ones that are efficient, safe, and actually make sense for everyday use.
What Is Level 3 EV Charging?
Level 3 charging—aka DC fast charging—is the fastest EV charging tech out there. It uses a high-power external module to send high-voltage DC power straight to your battery. It skips the vehicle’s onboard charger (OBC), so energy transfers way faster. A typical Level 3 DC fast charger (50kW–350kW) can get compatible EVs to 80% charge in 20–30 minutes.
Compare that to Level 1: it uses a standard 120V outlet, only 1.4–1.9kW. Level 2 runs on 240V AC (220V in China), 7–22kW. Both rely on your car to convert AC to DC—so they’re slow. Level 3’s big difference? The conversion happens in the charger, not your car. That’s why it’s “blazing fast.”

How Does a Level 3 Charger Work?
Plug into Level 1 or 2, and AC power flows into your car. Your onboard charger (OBC) turns it to DC to charge the battery.
With Level 3? All that conversion happens inside the charger. It has a built-in high-power rectifier and cooling system (liquid cooling for higher power). It turns grid AC power into DC power that matches your battery’s voltage. And it talks to your car’s battery management system (BMS) in real time—adjusting voltage and current so charging is fast and safe.
But this high-power, high-heat setup needs serious infrastructure: an independent high-voltage circuit, industrial-grade electrical panel, dedicated cooling, even liquid cooling. Commercial sites can handle that. Your home? Almost never.
Level 3 Charging vs. Other Charging Levels: 5 Key Differences
Charging Speed & Efficiency
| Charging Level | Typical Power | Range Per Hour | Time to Fully Charge a 200-Mile Battery |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | 1.4–1.9 kW | 3–5 miles | 40–100 hours |
| Level 2 | 7–22 kW | 25–80 miles | 3–10 hours |
| Level 3 | 50–350 kW | 180–600 miles | <1 hour |
By 2025, most home EVs have 60–100kWh batteries. Level 3 is way faster—but that speed comes with big tradeoffs.
Power Supply Requirements
Home electrical grids aren’t built for industrial loads. In North America, the average home uses single-phase 240V/200A—total available power around 48kW. In Chinese cities, most homes are single-phase 220V/63A—max 14kW. Even a 50kW Level 3 charger (the smallest) blows past those limits. Worse: Level 3 needs three-phase 400V/480V industrial power. Over 95% of homes don’t have that.
Installation Prerequisites
Installing a Level 3 charger needs hard requirements:
- An independent transformer or dedicated high-voltage line
- A fire-safe area that meets fire codes
- Approval from your local utility + grid capacity check
- Compliance with national electrical codes (like NEC 625, GB/T 18487.1)
These steps are slow and complicated. Most local building codes ban residential charging equipment over 22kW.
Cost Implications
Level 3 chargers are pricey—really pricey:
- Equipment: ¥50,000–¥300,000+ (about $7,000–$42,000)
- Electrical upgrades: New transformer or service line? ¥100,000–¥500,000+
- Civil work + permits: Cable installation, concrete, fire inspections—¥20,000–¥80,000
A Level 2 charger? Usually ¥8,000–¥25,000 total. Way better value.
Ideal Use Cases
Level 3 is for high-turnover, short-stay spots: highway rest stops, gas stations, logistics hubs, fast-food chains. Home charging is low-frequency, long-duration—mostly overnight. Average daily drive? 30–50 kilometers. Level 2 handles that easily. No need for extreme speed.
Can You Actually Install a Level 3 EV Charger at Home?
The short answer: Almost no. As of 2025, over 99% of standard homes worldwide can’t install a Level 3 EV charger at home—legally, safely, or affordably. Here’s why:
First, your grid can’t handle it. A 50kW charger’s instant power is like running 5 central AC units + 3 electric water heaters + all your lights at once. It’ll trip breakers or burn wires. Second, rules say no. Groups like the U.S. NFPA and China’s Ministry of Housing cap residential EV charging power—most areas max out at 22kW (single-phase) or 43kW (three-phase).
Rare exceptions: Detached villas with their own transformers—like some fancy California communities or rural European manors. But even then? Terrible ROI. A 150kW charger might get used less than 100 times a year. But you’ll pay hundreds of thousands for upgrades. Not worth it.
The True Cost of a Level 3 EV Charger at Home
Say you’re dead set on a 50kW Level 3 charger (the cheapest option). 2025 costs in China:
- Charger: ¥60,000
- Electrical upgrade (200kVA dedicated transformer): ¥200,000+
- Cable installation + construction: ¥50,000
- Fire safety + permits: ¥15,000
- Total: Over ¥325,000
With that money, you could install 10+ smart Level 2 chargers for an entire neighborhood. Plus, Level 3 chargers depreciate 10% a year. Maintenance is ¥5,000+ annually. Technology changes fast (hello 800V platforms). It’ll be obsolete in 5 years.
Level 3 Home Charging May Lead to High Electricity Bills
Initial cost isn’t the only problem. Level 3’s high power triggers “demand charges”—bills based on your monthly peak power use. For example:
- Base rate: ¥0.6/kWh
- Demand charge: ¥30/kW·month
A single 50kW charge peak? ¥1,500/month just in demand charges. That’s way more than the electricity itself. Even off-peak charging doubles your bill. Long term, Level 3 at home is bad for your wallet—and the grid.
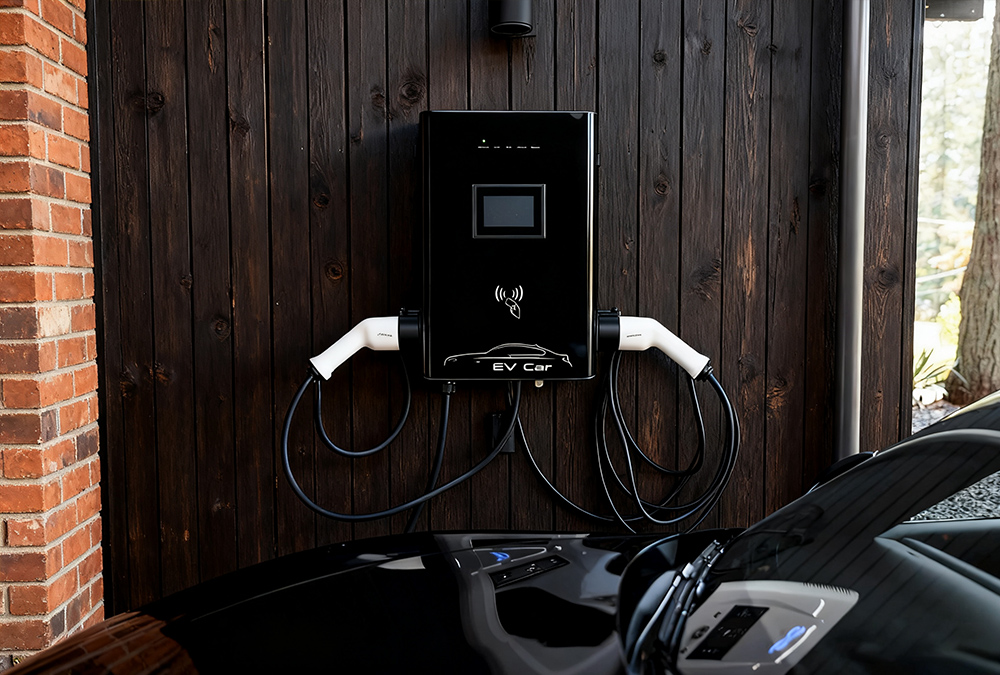

The Best Alternatives to a Level 3 EV Charger at Home
Level 2 Charging Solutions (7kW–22kW)
Level 2 is the sweet spot for home use. It balances speed, safety, and cost:
- 7kW charger: Full charge in 6–8 hours—perfect for overnight
- 11–22kW (three-phase): Full charge in 3–4 hours—great if you have three-phase power
- Easy install: Just a dedicated 220V/240V circuit. An electrician finishes in a day.
- Affordable: Total cost (equipment + install) usually under ¥20,000
Best part? Level 2 fits grid load curves. Use off-peak night rates (as low as ¥0.3/kWh in some areas) to save even more. AnengJi’s best level 2 ev charger for home has all these perks—plus smart features.
Portable & Hybrid Chargers
Renters, no fixed parking, or frequent travelers? Portable EV chargers (Portable EVSE) are perfect:
- Works with 10–16A current—fits standard and industrial outlets
- Lightweight (<3kg) and easy to store
- IP65 waterproof + overcurrent protection—safe to use
- High-end models have “hybrid mode”: 3.5kW slow charge at home (220V), 7kW fast charge at public 240V stations. Flexible for any scenario.
How to Choose the Right EV Charger for Your Home?
Pick a home EV charger by considering these:
- Vehicle compatibility: Check your car’s max OBC acceptance power (e.g., Tesla Model Y is 11.5kW)
- Electrical setup: Single-phase or three-phase? Does your electrical panel have extra capacity?
- Installation space: Wall-mounted saves room; floor-standing is movable
- Smart features: Scheduled charging, remote control, energy stats—make life easier
Stick to brands with UL, CE, or CCC certification. Look for a good warranty—quality brands offer 3+ years. AnengJi’s smart ev charger with wifi checks all these boxes.
Explore AnengJi’s Fast Charging Solutions
We’ve been in the charging industry for over 20 years. AnengJi offers EV charging products for every scenario:
- Home Level 2 Wallbox: 7kW–22kW, Wi-Fi/4G remote management, IP65 protection. Works with Tesla, BYD, NIO, XPeng, and more.
- Commercial Level 3 Fast Chargers: 60kW–360kW, liquid-cooled supercharging, dual-gun smart distribution. Great for businesses, properties, and public stations.
- Safety & Smarts: Built-in overvoltage, overcurrent, leakage, and temperature protection. Monitor charging in real time via app.
Our philosophy? Level 2 for home, Level 3 for commercial use. We help you avoid overspending—get exactly what you need. As a trusted wallbox charger manufacturer and china ev charger supplier, we deliver reliable home ev charging solutions.
Conclusion
Here’s the bottom line: Installing a Level 3 EV charger at home isn’t feasible—technically, legally, or financially. It’s a “nice idea” that doesn’t work for real life. For 99% of home users, a 7–22kW Level 2 charger is the way to go. It handles daily commutes and weekend trips. You’ll save money with off-peak rates and government subsidies. Leave Level 3 charging to public spots—highways, malls, gas stations—where professional operators can manage it. Smart EV owners use the right charger for the right place. That’s how you make electric mobility work for you.
Related Posts

EV Charging Business Opportunities: 2026 Profitability Guide
News
8 Reasons to Install a Level 2 Car Charger at Home
News



Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!