Introduction
As electric vehicles take over roads worldwide, one question keeps coming up: “How long do EV batteries last?”
It’s a fair question — after all, the battery is the heart of every EV.
In this guide, we’ll break down how EV batteries work, what affects their lifespan, how degradation happens over time, and what you can do to maintain and extend their life.
By the end, you’ll understand how to get the most out of your EV and make smarter, longer-lasting choices.
How EV Batteries Work
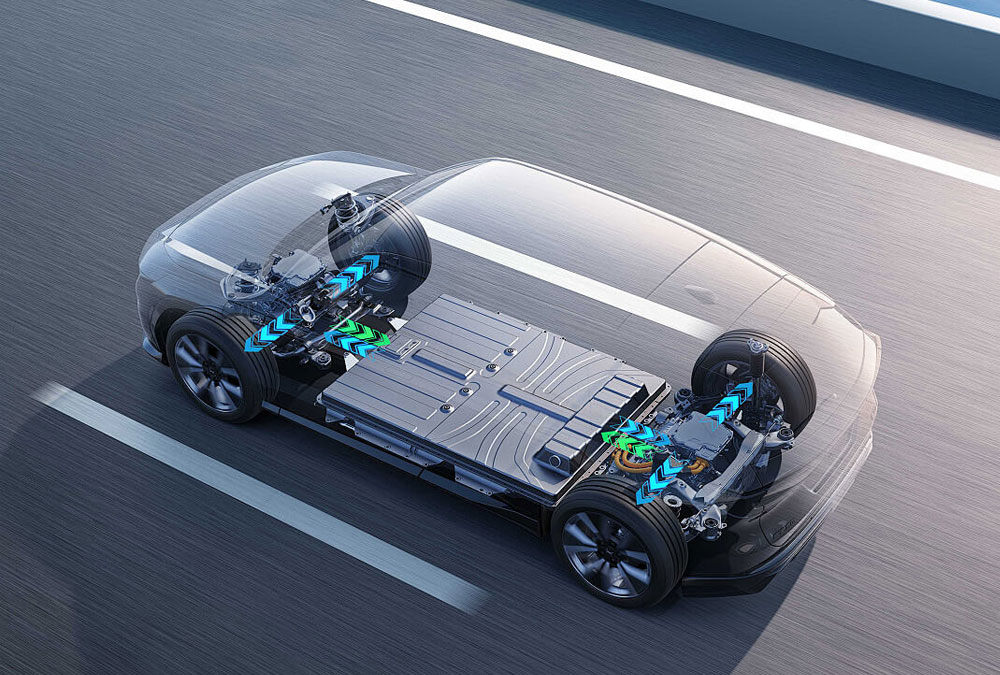
When you plug in your EV, electricity is stored in a high-voltage traction battery pack. During driving, this energy is sent through a controller to the electric motor, which turns it into motion.
Most modern EVs also feature regenerative braking, a system that captures some of the energy normally lost during braking and feeds it back into the battery — improving efficiency.
Today’s EVs mainly use lithium-ion batteries, similar to those in your phone but much larger and more advanced. Each battery has a positive electrode (nickel-cobalt-manganese or lithium iron phosphate), a negative electrode (graphite), an electrolyte, and a separator. During charging and discharging, lithium ions move between electrodes — storing and releasing energy.
This design provides high energy density, low self-discharge, and long cycle life, which makes it ideal for electric vehicles.
Unlike gas cars that rely on internal combustion, EVs run purely on electricity.
Gasoline vehicles are measured in miles per gallon (MPG), while EVs use kilowatt-hours per 100 kilometers (kWh/100km). Most EVs also have a smaller 12-volt battery for powering electronics like lights and infotainment — just like in traditional cars.
EVs vs Gas Cars — Simpler, Cheaper, Cleaner
EVs have far fewer moving parts. They don’t need oil changes, spark plugs, or exhaust systems. Thanks to regenerative braking, even the brake pads last longer.
The result? Energy efficiency of over 85%, compared to 20–30% for gasoline vehicles.
Although the initial purchase price of an EV is higher, long-term maintenance costs are much lower.
According to the U.S. Department of Energy, EV owners spend about 40% less on maintenance than gas car owners.
And here’s the good news — most modern EV batteries can last 10 to 20 years, often outliving the car itself.
Environmentally, EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions. When charged with renewable energy, their carbon footprint drops even further.
While battery manufacturing does consume resources, improvements in recycling and cleaner production methods are making EVs more sustainable than ever.
What Causes EV Battery Degradation?
Every EV battery slowly loses capacity over time — a process known as EV battery degradation.
When a battery’s usable capacity drops below about 80% of its original design, it’s considered the end of its “first life.”
Your EV will still drive just fine, but range may shrink, and charging can take a little longer.
So what affects EV battery lifespan the most?
Mainly temperature, charging habits, fast-charging frequency, and driving patterns.
- Heat speeds up chemical reactions inside the battery, breaking down the electrolyte faster. Anything above 104°F (40°C) can cause permanent damage.
- Cold temperatures slow down the ions inside the cell, reducing efficiency and making charging slower.
- Regularly charging to 100% or draining to 0% puts extra stress on the electrodes.
- Frequent DC fast charging (also known as rapid charging) can increase internal heat, reducing lifespan by as much as 15–20% over time.
Most lithium-ion EV batteries are rated by charge cycles.
- NMC or NCA batteries last about 1,500–2,000 cycles
- LFP (lithium iron phosphate) batteries can reach 2,000–3,000 cycles
Keeping your charge between 20% and 80% is the easiest way to extend battery life.
Modern EVs also use Battery Thermal Management Systems (BTMS) to keep the pack between 68°F and 104°F (20°C–40°C).
Data shows that liquid-cooled batteries like those in the Tesla Model S degrade by only 2.3% per year, while air-cooled systems like in the Nissan Leaf lose about 4.2% per year — proof that cooling matters.
Types of EV Batteries and Their Lifespan
Different types of EV batteries have different performance traits, costs, and lifespans. Here’s a breakdown:
| Battery Type | Cycle Life | Estimated Lifespan | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| NMC/NCA (Nickel-based Lithium-ion) | 1,500–2,000 | 6–8 years | High energy density, good low-temp performance, common in premium EVs |
| LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) | 2,000–3,000 | 8–12 years | Safer, cheaper, heat-resistant; used in BYD and Tesla Model 3 RWD |
| Nickel-Metal Hydride | <1,000 | 3–5 years | Used in early hybrids, now mostly phased out |
| Solid-State (Future) | >3,000 (expected) | 15+ years | Higher density, ultra-safe, in testing phase |
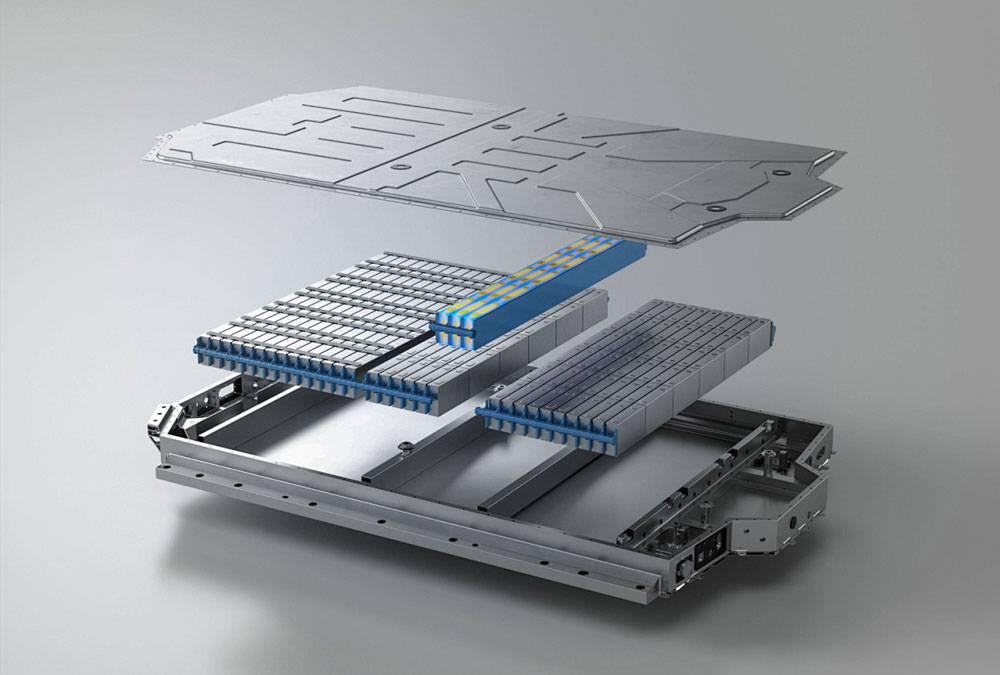
Each battery pack is built from cells → modules → packs, managed by a Battery Management System (BMS).
The BMS constantly monitors voltage, temperature, and State of Charge (SOC) to prevent overcharging, overheating, and other safety issues.
In short:
- NMC/NCA is ideal for drivers who need long range and performance — but requires precise thermal control.
- LFP is perfect for daily commuters or hot climates — it’s safer, cheaper, and more stable.
Average EV Battery Lifespan
Research shows modern EV batteries age slower than ever.
A study by Geotab on over 10,000 vehicles found an average annual degradation rate of just 1.8%.
That means after 10 years, most EVs still have about 82% of their original capacity.
Real-world data supports this too — many Tesla Model S cars with over 200,000 miles (300,000 km) still retain 85%+ battery health.
Most automakers now offer 8-year / 100,000–150,000-mile battery warranties (Tesla, Hyundai, Kia, etc.), guaranteeing at least 70–80% capacity retention during that period.
Climate also plays a big role:
EVs in cooler regions like Norway can last 15+ years, while those in hot areas like Arizona may see reduced lifespans (around 8–10 years).
Interestingly, high mileage alone doesn’t kill a battery — it’s heat and charging habits that matter most.
Why EV Batteries Degrade Over Time
So what’s actually happening inside?
Battery degradation is mostly caused by chemical aging — microscopic damage to the anode and cathode materials.
Over time, the SEI (Solid Electrolyte Interface) layer thickens, the electrolyte slowly breaks down, and lithium ions get trapped, reducing the battery’s active capacity.
This process happens in two ways:
- Calendar Aging – Even when the battery isn’t used, chemical reactions continue inside, causing about 1–2% loss per year.
- Cycle Aging – Each charge and discharge slightly wears out the battery materials.
By managing your usage patterns, you can make calendar aging the main factor — meaning your battery wears out much slower.
Signs your battery is aging include:
- Noticeable range loss (especially faster in winter)
- Slower charging speeds
- Dashboard alerts about “reduced battery performance”
- Fast chargers delivering less power than before
How to Extend EV Battery Life
The good news? You have more control over your EV battery’s lifespan than you might think.
With a few simple habits, you can extend EV battery life for years — even decades.
Here’s how:
Keep charge between 20%–80%.
Daily commuting doesn’t require a full charge. Top up to 90–100% only before long trips.
Avoid leaving your EV fully charged overnight, especially in hot weather.
Use Level 2 home charging whenever possible.
Slow charging is gentler on the cells. Save fast charging for road trips or emergencies.
Try to limit DC fast charging to no more than 30% of your total sessions.
Park smart.
In summer, use shaded parking or a garage to prevent heat buildup.
In winter, preheat the battery before charging — most EVs can do this automatically.
Store your EV properly if unused.
Keep the battery around 50% charge and store it in a cool, dry place (50°F–77°F / 10°C–25°C).
Check the State of Charge (SOC) once a month to prevent the 12V battery from draining.
Drive smoothly and reduce weight.
Hard acceleration drains power and increases battery stress.
Lighten your load and use low rolling-resistance tires to improve range and efficiency.
Modern EVs also receive over-the-air (OTA) updates, allowing automakers to optimize battery performance, thermal management, and even charging limits.
Tesla, BYD, and Hyundai all use this technology to help owners maintain electric car battery health automatically.
What Happens When an EV Battery Wears Out?
Even when an EV battery’s capacity drops below 80%, it’s far from useless.
Most “retired” EV packs still have years of life left for stationary energy storage — powering homes, buildings, or grid backup systems.
These second-life applications can extend a battery’s usefulness by another 4–16 years.
By 2030, over 85 million EVs worldwide will reach end-of-life, making EV battery recycling and reuse a cornerstone of the circular economy.
When recycling, key materials like lithium, nickel, and cobalt are recovered and reused in new batteries — cutting mining demand and lowering environmental impact.
Governments in China, the EU, and the U.S. now require automakers to build recycling systems that close the loop from production to reuse.
Advanced recovery technologies such as hydrometallurgical and direct recycling can achieve up to 95% recovery rates, dramatically reducing waste and production costs.
This shift not only improves sustainability but also helps lower EV battery replacement cost in the future.
Can EV Batteries Be Replaced?
Yes — EV batteries can be replaced, though most drivers won’t need to for 15–20 years.
You’ll only need to consider replacement if capacity falls below 70% or the car displays system fault codes.
Currently, EV battery replacement cost ranges between $4,000 and $20,000, depending on brand and pack size.
That sounds steep, but costs are falling fast — analysts predict prices will drop by 40% or more by 2030 as recycling and mass production expand.
Some third-party shops offer module-level refurbishment at half the price of full replacement, but compatibility and warranty coverage can be risky.
OEM replacement, though more expensive, ensures full safety and system integration.
EV Battery Safety and Maintenance
Modern EVs are built with safety in mind.
Battery packs are sealed and reinforced, featuring thermal runaway prevention, automatic shutdown systems, and overcharge protection.
Statistically, EVs are much safer than gas cars —
data shows only 25 EV fires per 100,000 vehicles, compared to 1,530 fires per 100,000 gasoline cars.
To keep things safe:
- Regularly inspect your 12V auxiliary battery, as it powers startup systems.
- Avoid bottom scrapes since most packs are mounted under the floor.
- Always use certified or OEM-approved chargers to protect the Battery Management System (BMS).
- Choose ISO 15118-compliant charging stations for secure communication and reliable charging.
Public DC fast chargers should be serviced regularly to maintain cooling efficiency and safe voltage operation.
The Future of EV Battery Technology
The future of electric vehicle battery technology is exciting and fast-moving.
- Solid-state batteries are coming.
They use solid electrolytes instead of liquid ones, improving energy density by 50%+, allowing faster charging and reducing fire risks.
Toyota and CATL plan to launch mass production between 2027–2030. - 800V high-voltage platforms, already used by Porsche and XPeng, allow ultra-fast charging —
200 km (124 mi) of range in just 5 minutes. - New materials like silicon anodes, cobalt-free cathodes, and self-healing electrolytes promise longer life and lower cost.
Combined with AI-driven BMS systems, the next generation of EVs may last 25 years or more with minimal degradation.
Final Thoughts — Getting the Most Out of Your EV Battery
A well-cared-for EV battery can easily outlive the car itself.
Treat it right, and it’ll reward you with consistent range, low running costs, and peace of mind.
Remember these golden rules:
- Stay between 20%–80% charge most of the time.
- Use slow charging whenever possible.
- Avoid extreme heat and cold.
- Drive gently and use regenerative braking.
Small habits make a big difference — ten years down the road, you’ll still be driving on a battery that performs almost like new.
Choosing an EV isn’t just a smart decision — it’s an investment in a cleaner, more sustainable future.
FAQ – EV Battery Lifespan, Maintenance & Recycling
1. How long do EV batteries really last?
Most modern EV batteries last between 10 and 20 years, depending on climate, charging habits, and driving style.
Data from Tesla and Hyundai shows an average annual degradation of only 1.5%–2%, meaning your battery can retain 80% of its capacity after a decade.
With proper care and balanced charging, an electric car battery life can even exceed the vehicle’s lifetime.
2. What causes EV battery degradation over time?
Battery degradation happens naturally as cells go through charge cycles.
High temperatures, frequent DC fast charging, and fully charging to 100% can speed up chemical wear.
Using Level 2 slow charging and keeping your battery between 20%–80% helps extend EV battery life and maintain long-term health.
3. How much does it cost to replace an EV battery?
The EV battery replacement cost depends on the car model and capacity.
On average, replacement ranges from $4,000 to $20,000.
However, battery prices are dropping quickly — experts expect costs to fall by 40% before 2030 thanks to recycling and mass production.
Some automakers even offer 8–10 year warranties covering up to 160,000–240,000 km.
4. Does fast charging damage EV batteries?
Not immediately, but frequent fast charging can raise battery temperature and speed up lithium-ion battery degradation by 15–20% over time.
Using fast chargers occasionally (for long trips) is perfectly fine.
For daily charging, stick to Level 2 or home chargers to keep your battery in top condition.
5. Can EV batteries be recycled or reused?
Yes — today’s EV battery recycling technology can recover up to 95% of valuable materials such as lithium, nickel, and cobalt.
Batteries that drop below 80% capacity can be repurposed for energy storage, powering homes or grids for another 5–10 years.
This circular process greatly reduces environmental impact and helps lower future EV battery costs.
6. What’s the best way to maintain electric car battery life?
- Avoid extreme heat or cold.
- Keep charge levels between 20–80%.
- Use slow charging more often than fast.
- Don’t leave your EV plugged in overnight when full.
- Update your car software regularly for improved battery management system (BMS) control.
These small steps can extend your EV battery lifespan and save you thousands over time.
7. How can I tell if my EV battery is aging?
Common signs include reduced driving range, slower charging speeds, or battery warnings on your dashboard.
If your range drops by more than 25% or charging time doubles, it’s time to run a battery health check.
Most EVs now have built-in battery health monitoring tools accessible through mobile apps.






Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!