Introduction: Understanding Level 1 EV Charging
As electric vehicles become part of daily life, many new owners wonder how to charge their cars at home. Just as gas cars use different fuel grades, EVs have different “charging levels”—Level 1, Level 2, and DC Fast Charging.
Among them, the Level 1 EV charger stands out as the simplest, most affordable, and most accessible solution for everyday use.
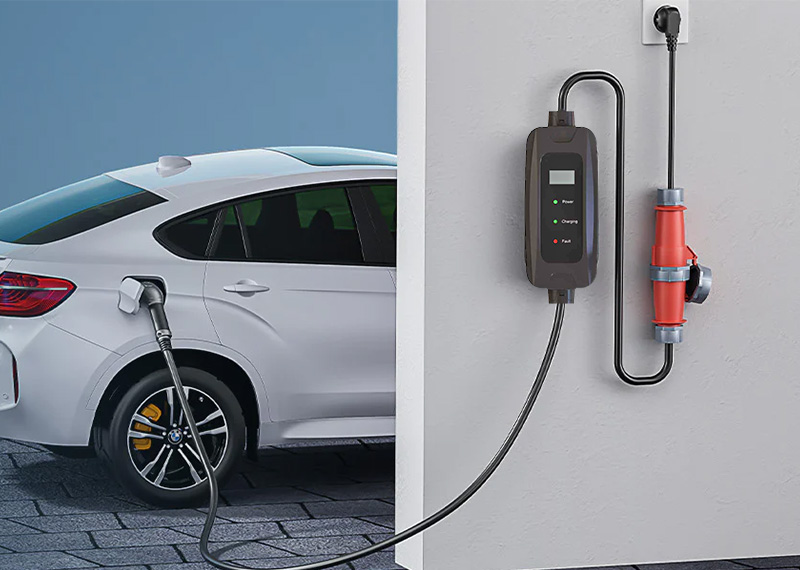

It doesn’t require special installation—just a regular 120V household outlet. This makes it an ideal option for new EV owners, short-distance commuters, and anyone looking for an easy way to start home EV charging.
What Is a Level 1 EV Charger?
A Level 1 EV charger uses a standard 120-volt (120V AC) outlet to charge your electric vehicle. It’s the same kind of outlet you’d plug in your phone or laptop.
Most electric cars include a portable charging cable with a J1772 connector (for non-Tesla vehicles). You simply plug one end into your car’s charging port and the other into a grounded wall socket—charging begins automatically.
Because it requires no professional installation or additional wiring, Level 1 charging remains the most economical home EV charging solution, especially for users with moderate daily driving distances.
How Does Level 1 EV Charging Work?
Every major EV brand sold in North America (except Tesla) uses the SAE J1772 charging connector. Tesla models use a proprietary port, but you can easily charge them with a J1772 adapter.
When plugged into a standard 120V AC outlet, the vehicle’s onboard charger (OBC) converts the alternating current into direct current (DC) to store energy in the battery. Once full, the car automatically stops charging to prevent overfill or energy waste.
It’s a true plug-and-play experience—simple, safe, and reliable.
How Fast Is Level 1 EV Charging?
Level 1 charging delivers around 1.3–2.4 kW of power, adding about 3–5 miles of range per hour.
For example:
- A Nissan Leaf or Chevy Bolt can gain roughly 30–40 miles of range overnight (about 8 hours).
- A completely empty 60 kWh battery may take 20–24 hours to reach full charge.
That’s why Level 1 EV charging is best for overnight top-ups or daily commutes under 40 miles. It’s not ideal for long-distance travel or rapid battery recovery.
When Is Level 1 Charging the Best Option?
While Level 1 charging is the slowest type, it’s perfect in several situations:
For Daily Short Commutes
If you drive less than 20 miles a day, Level 1 charging easily replenishes your battery overnight.
For Plug-in Hybrid Owners (PHEVs)
Cars like the Toyota Prius Prime or Honda Clarity PHEV have smaller batteries (8–15 kWh), so Level 1 chargers can fully recharge them in just a few hours.
For Homes Without 240V Access
If you live in an apartment or rental property where you can’t install a 240V outlet, Level 1 charging is your go-to solution. All you need is a grounded 120V socket.
As an Emergency Backup
Traveling? Staying at a friend’s house? A portable EV charger lets you plug into any outlet for emergency top-ups. That flexibility makes Level 1 charging a dependable backup option.
How Much Does Level 1 Charging Cost?
One of its biggest advantages is low cost.
Most EVs come with a free portable charging cable, and since you use your existing electrical circuit, there’s no need for professional installation.
Using average U.S. electricity rates (about $0.15 per kWh), fully charging a 60 kWh EV battery costs around $9–$12—a fraction of the cost of refueling a gas car.
Even if you decide to install a dedicated 120V outlet, it usually costs $125–$300, far cheaper than installing a full Level 2 station.
Level 1 vs Level 2 vs DC Fast Charging
| Charging Type | Voltage | Power Output | Range per Hour | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | 120V AC | 1.3–2.4 kW | 3–5 miles | Home overnight or emergency |
| Level 2 | 240V AC | 3.3–19.2 kW | 15–60 miles | Home, workplace, public lots |
| DC Fast Charging | 200–1000V DC | 50–350 kW | 60–300+ miles | Highways, commercial hubs |
⚠️ Note: Some vehicles, like Fiat 500e or Prius Prime, do not support DC fast charging. Using high-power stations on small batteries may reduce long-term health.
The Drawbacks of Level 1 Charging
- Slow charging speed – not ideal for long trips or full battery recovery.
- Limited amperage (usually 12A) – can’t fully utilize higher onboard charger capacity.
- Outlet safety – continuous overnight charging requires grounded, safe connections.
If you want faster and more efficient daily charging, consider upgrading to a Level 2 EV charger from a trusted supplier like AnengJi.
The Future of EV Charging Standards
With the rise of the NACS (North American Charging Standard), many automakers—Ford, GM, BMW, Mercedes, and more—are shifting toward Tesla’s connector design.
Still, Level 1 EV chargers remain universal for any car that supports AC charging. Using an adapter, you can continue to charge safely through any 120V outlet.
Final Thoughts — Why Level 1 EV Charging Still Matters
Level 1 charging may not be fast, but it’s accessible, affordable, and convenient.
It’s perfect for:
- Short-distance commuters
- Plug-in hybrid drivers
- Apartment or rental residents
- Anyone needing a reliable emergency backup
As charging infrastructure expands, Level 1, Level 2, and DC fast chargers will work together to support every EV user’s needs.
If you’re looking for OEM/ODM EV chargers, J1772 connectors, or smart home charging systems, AnengJi provides complete EV charging solutions for residential, commercial, and fleet use.
📩 Contact us today to get a free product guide or OEM quote.
FAQ — Common Questions About Level 1 EV Chargers
Q1: What is a Level 1 EV charger?
A Level 1 EV charger uses a 120V AC outlet to charge electric vehicles. It’s included with most EVs and perfect for home or overnight charging.
Q2: How fast is Level 1 EV charging?
It adds about 3–5 miles of range per hour, depending on your EV’s battery size and charging efficiency.
Q3: Can I charge my EV with a regular wall outlet?
Yes. Level 1 chargers plug directly into any grounded 120V outlet, no special setup required.
Q4: Is Level 1 charging enough for daily commuting?
If your commute is under 40 miles per day, overnight Level 1 charging is perfectly sufficient.
Q5: How much does Level 1 charging cost at home?
On average, it costs around $9–$12 to fully charge a 60 kWh EV battery using Level 1 charging at home.
Q6: What’s the difference between Level 1 and Level 2 charging?
Level 2 chargers use 240V power and charge 3–5 times faster, but require professional installation.
[post_navigation]






Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!